What happens when a developing country grows its clean energy faster than most of the West, but doesn’t slow down its GDP goals?
India is the third biggest energy user in the world, and it is going through a green transition that is not only fast, but also furious. Solar panels are shining on rooftops, new businesses are riding the wave of clean energy, and even old power companies like NTPC are going D2C in clean energy.
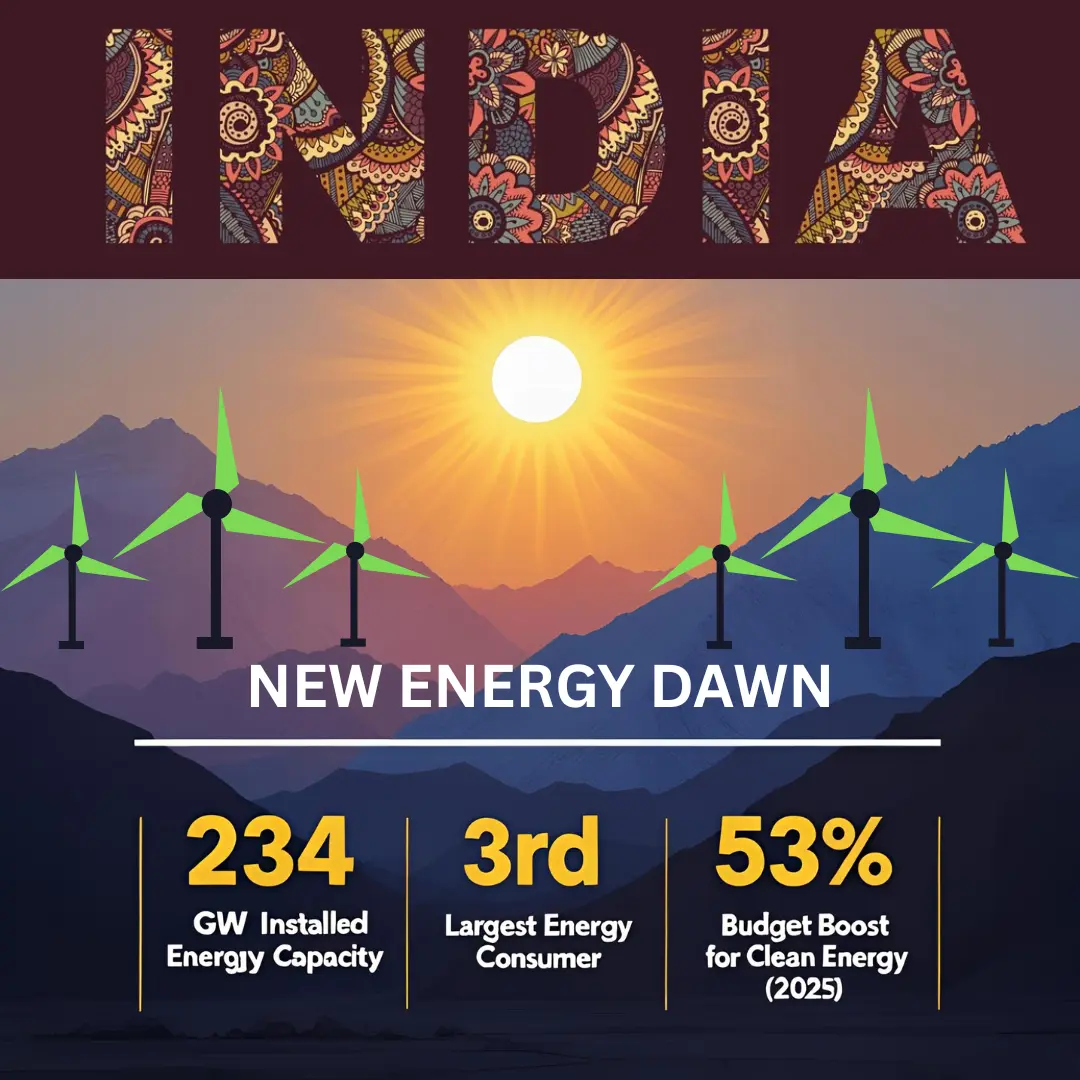
India’s renewable energy sector isn’t just about climate goals in 2025. It’s a mix of grabbing market share, getting investors excited, having strong policies, and changing the economy. This is no longer a sunrise sector; it has grown from 0 to 234 GW in just over a decade. It’s noon.
So, what is driving India’s push for renewable energy? Let’s look at the capacity numbers, policy changes, business shifts, and big bets that will change India’s energy story in 2025.
The Numbers That Matter: Installed Capacity Snapshot (Mid-2025)
India’s renewable capacity is clocking record numbers. By mid-2025:
- Total renewable capacity (including large hydro): ~234 GW
- Solar: ~116 GW (ground-mounted, rooftop, off-grid, hybrid)
- Wind: 51.7 GW
- Biomass (bagasse + other): 11.7 GW
- Small hydro: 5.1 GW
- Large hydro: 49.4 GW
FY2024–25 was a record-breaker — India added 29.5 GW of renewable capacity. In just the first half of 2025, it installed another 22 GW (mostly solar/wind) — a whopping 56% YoY jump.
| Resource | Installed Capacity (GW) |
|---|---|
| Solar | 116.25 |
| Wind | 51.67 |
| Small Hydro | 5.10 |
| Biomass (bagasse + other) | 10.74 |
| Waste-to-Energy (incl. off-grid) | 0.85 |
| Total (excl. large hydro) | 184.61 |
| Large Hydro | 49.38 |
| Grand Total (all RE) | 233.99 |
In terms of electricity generation (not capacity), renewables made up about 24.4% of the power produced in Q4 FY2024-25. Coal and thermal, on the other hand, still made up a large ~71%. But here’s the twist: non-fossil fuel capacity has officially passed fossil fuel capacity.
Policy Push: What’s Powering the Growth?
Behind this growth is a cocktail of bold government targets, fiscal muscle, and regulatory tailwinds.
Big Goals
- 500 GW of non-fossil capacity by 2030
- Net-zero emissions by 2070
- 50% electricity from non-fossil sources by 2030 (Paris Agreement pledge)
Budget Firepower (2025–26)
- MNRE allocation: ₹26,549 crore (+53% from FY25 RE)
- PM Surya Ghar: ₹20,000 crore (+80%) for rooftop solar
- PM-KUSUM: Funds for solarizing agriculture pumps
- Green Hydrogen Mission: ₹600 crore (up from ₹300 crore)
- India’s clean energy surge mirrors innovation trends seen in the bootstrapped rise of Micro SaaS in India, where lean operations meet big vision — a synergy evident in the renewable sector too.
New Policy Highlights
- Storage Transmission Waiver: 100% waiver on ISTS for battery/pumped hydro projects until June 2028
- ₹54,000 crore battery storage scheme (30 GWh)
- PLI schemes for domestic solar module production
- Green bonds and green deposits for sustainable finance
- 100% FDI allowed in RE generation and distribution
It’s clear that India isn’t just pushing renewables forward. It’s pushing them with all its might.
Market Structure: Who’s Winning the Clean Energy Race?
India’s RE market is now a tight but growing race between big corporates, state utilities, and hungry private developers.
Solar
- Adani Green Energy: ~2.6 GW added (2024), 17.6% market share
- ReNew Power: 1.6 GW
- ACME Solar: 1.2 GW
- NTPC REL, O2 Power are also major players
Together, the top 5 controlled ~52% of solar capacity additions in 2024.
Wind
- Manufacturers: Suzlon, Inox Wind, Vestas, GE, Siemens Gamesa
- Developers: ReNew, Mytrah, SJVN Green Energy
- New leases: 4 GW of offshore wind zones earmarked (2025)
Institutional Power Players
- SECI/PM-SMART: Govt-backed tendering and park development
- NTPC: Pivoting fast with its own RE arm
- State discoms: Back in the game, setting up solar parks and hybrid plants

Investment Trends: Green is the New Gold
Massive policy bets are only part of the story. Equally striking is the sheer flood of capital into renewables.
Public Lending Muscle
- IREDA loan book: ₹76,250 crore in FY24–25 (+28% YoY)
- ₹47,453 crore in new loan sanctions
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- FDI inflow (FY25): ~$3.4 billion (8x growth since FY21)
- Green bonds: ~$10 billion raised in 2023 alone
- Sovereign green bonds: ₹57,697 crore in FY22–25
Big Numbers Ahead
- Projected investment needed by 2030: ₹30–46 lakh crore ($400–600 billion)
- Just like Indian startups use growth hacks to scale rapidly in 2025, renewable energy developers are leveraging green bonds, policy incentives, and private PPAs for exponential expansion.
Key Investment Trends
- Private PPAs signed by Google, Amazon, Tata Steel, etc.
- Bids from global infra funds keep pushing solar tariffs down
- Climate bonds, ESG funds, and new carbon markets (under draft CCTS bill) are shaping capital flows
What’s Next? Tech, Trends & Disruption
India’s RE future isn’t just about megawatts. It’s about megatrends:
1. Energy Storage Takes Center Stage
- Less than 5 GW of battery/pumped storage today
- But 27 GW of pumped hydro in the pipeline
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) scheme launched (₹54,000 cr budget)
2. Green Hydrogen Goes Mainstream
- 5 MMT annual production target by 2030
- Electrolyser plants planned nationwide
- Doubling of hydrogen mission budget in 2025
3. Rural + Off-grid Solar Boom
- Rooftop solar under PM Surya Ghar
- Solar pumps via PM-KUSUM
- Mini/micro grids for energy access
4. Hybrid, Floating, and RTC Projects
- Round-the-clock auctions with solar+wind+storage are the new normal
- Floating solar parks are gaining traction (especially in states like Kerala and Maharashtra)
5. Smart Grids + Digital Tech
- AI for load forecasting
- IoT for distributed energy monitoring
- Demand-response pilots underway in Delhi, Mumbai
This short video will show you how India reached a big clean energy goal: by the end of 2025, more than half of its energy will come from sources other than fossil fuels. It highlights the pace, policy shifts, and market forces driving this transformation. A great picture of the green transition in action.
Challenges: Where the Sun Doesn’t Shine (Yet)
Yes, India’s growth is exciting, but let’s not gloss over the realities:
- Coal still supplies ~75% of electricity (generation vs. capacity mismatch)
- Module imports: ~85% still come from China
- Battery imports: Over 80% imported
- Financing capacity: Huge investment gaps (~₹32 lakh crore needed by 2030)
- Pollution impact: 1.6 million deaths linked to air pollution (2021)
- Low utilization: Storage and curtailment limit RE performance
The bottom line? India needs more than just shiny targets. It needs domestic manufacturing, resilient financing, and a reliable grid.
Final Word: Green Growth or Green Gamble?
India’s clean energy story in 2025 is like a cricket match in the final overs — fast-paced, high-stakes, and impossible to ignore. The scoreboard is impressive. The policy captaincy looks focused. But the game is far from over.
If it sustains 50–60 GW of RE additions annually, India will likely cross 500 GW of non-fossil capacity by 2030. The opportunity? A global leadership role in the clean economy. The risk? Falling behind if storage, manufacturing, and policy clarity don’t keep pace.
This rapid transformation of India’s energy landscape is as disruptive as the competition between FMCG giants and D2C brands in India, where agility and innovation redefine legacy systems — just like how clean energy is rewriting the power sector’s rulebook.
Either way, India’s renewable energy sector in 2025 isn’t just an industry story. It’s a business case, a policy thesis, and a societal shift — all rolled into one electric future.
Sources
- MNRE – Renewable Energy Physical Progress in India
- PIB – India’s Clean Energy Sector in Budget 2025
- Economic Times – India’s Record Renewables Rollout Towards 2030 Goal
- ET EnergyWorld – India’s Renewable Energy Output Hits 1249 BU in Q4 FY2024-25
- ET Edge Insights – India’s Shift to a Non-Fossil Fuel Future
- Wikipedia – Renewable Energy in India
- Moneycontrol – Budget 2025 Increases Green Energy Allocation by 53%
- Reuters – India Extends Transmission Charge Waiver for Energy Storage
- Renewable Watch – India’s Wind Energy Strategy and Expansion Targets
- Mercom India – Top Utility-Scale Solar Developers in 2024
- EQ Mag – IREDA Loan Sanctions Rise 27% in FY 2024-25



